A G.Vivek Venkatesh blog to help Anna University Computer Science and Engineering Students.
Tuesday, September 21, 2010
Packet Capturing using Raw Socket Program
Program using Raw Sockets(like Packet Capturing)
Note
You must have root privilege in order to run this program.
Download Source Code(preferred than viewing it Live on blog)
program
output
Program
(rawudp.c)
#include "unistd.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "sys/socket.h"
#include "netinet/ip.h"
#include "netinet/udp.h"
#define PCKT_LEN 8192
// The IP header's structure
struct ipheader {
unsigned char iph_ihl:5, iph_ver:4;
unsigned char iph_tos;
unsigned short int iph_len;
unsigned short int iph_ident;
unsigned char iph_flag;
unsigned short int iph_offset;
unsigned char iph_ttl;
unsigned char iph_protocol;
unsigned short int iph_chksum;
unsigned int iph_sourceip;
unsigned int iph_destip;
};
// UDP header's structure
struct udpheader {
unsigned short int udph_srcport;
unsigned short int udph_destport;
unsigned short int udph_len;
unsigned short int udph_chksum;
};
// Function for checksum calculation.
unsigned short csum(unsigned short *buf, int nwords)
{ //
unsigned long sum;
for(sum=0; nwords>0; nwords--)
sum += *buf++;
sum = (sum >> 16) + (sum &0xffff);
sum += (sum >> 16);
return (unsigned short)(~sum);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int sd;
char buffer[PCKT_LEN];
// Our own headers' structures
struct ipheader *ip = (struct ipheader *) buffer;
struct udpheader *udp = (struct udpheader *) (buffer + sizeof(struct ipheader));
// Source and destination addresses: IP and port
struct sockaddr_in sin, din;
int one = 1;
const int *val = &one;
memset(buffer, 0, PCKT_LEN);
// Create a raw socket with UDP protocol
sd = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_UDP);
if(sd < sin_family =" AF_INET;" sin_family =" AF_INET;" sin_port =" htons(atoi(argv[2]));" sin_port =" htons(atoi(argv[4]));" s_addr =" inet_addr(argv[1]);" s_addr =" inet_addr(argv[3]);">iph_ihl = 5;
ip->iph_ver = 4;
ip->iph_tos = 16;
ip->iph_len = sizeof(struct ipheader) + sizeof(struct udpheader);
ip->iph_ident = htons(54321);
ip->iph_ttl = 64; // hops
ip->iph_protocol = 17; // UDP
ip->iph_sourceip = inet_addr(argv[1]);//Source IP address
ip->iph_destip = inet_addr(argv[3]);// destination IP address
// Fabricate the UDP header.
udp->udph_srcport = htons(atoi(argv[2]));//source port
udp->udph_destport = htons(atoi(argv[4]));//destination port
udp->udph_len = htons(sizeof(struct udpheader));
// Calculate the checksum
ip->iph_chksum = csum((unsigned short *)buffer, sizeof(struct ipheader) + sizeof(struct udpheader));
if(setsockopt(sd, IPPROTO_IP, IP_HDRINCL, val, sizeof(one)) < count =" 1;">iph_len, 0, (struct sockaddr *)&sin, sizeof(sin)) < 0)
{
perror("sendto() error");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
printf("Count #%u - sendto() is OK.\n", count);
sleep(2);
}
}
close(sd);
return 0;
}
Sunday, September 19, 2010
Remote Procedure Call Program in C
To implement Remote Procedure Call, and perform addition and subtraction of two numbers.
(Explanation will be given soon).
Program
simp.x
#define VERSION_NUMBER 1
%#define foo 127
struct operands {
int x;
int y;
};
program SIMP_PROG {
version SIMP_VERSION {
int ADD(operands) = 1;
int SUB(operands) = 2;
} = VERSION_NUMBER;
} = 555555555;
simpclient.c
/* RPC client for simple addition example */
#include "stdio.h"
#include "simp.h" /* Created for us by rpcgen - has everything we need ! */
/* Wrapper function takes care of calling the RPC procedure */
int add( CLIENT *clnt, int x, int y) {
operands ops;
int *result;
/* Gather everything into a single data structure to send to the server */
ops.x = x;
ops.y = y;
/* Call the client stub created by rpcgen */
result = add_1(&ops,clnt);
if (result==NULL) {
fprintf(stderr,"Trouble calling remote procedure\n");
exit(0);
}
return(*result);
}
/* Wrapper function takes care of calling the RPC procedure */
int sub( CLIENT *clnt, int x, int y) {
operands ops;
int *result;
/* Gather everything into a single data structure to send to the server */
ops.x = x;
ops.y = y;
/* Call the client stub created by rpcgen */
result = sub_1(&ops,clnt);
if (result==NULL) {
fprintf(stderr,"Trouble calling remote procedure\n");
exit(0);
}
return(*result);
}
int main( int argc, char *argv[]) {
CLIENT *clnt;
int x,y;
if (argc!=4) {
fprintf(stderr,"Usage: %s hostname num1 num\n",argv[0]);
exit(0);
}
/* Create a CLIENT data structure that reference the RPC
procedure SIMP_PROG, version SIMP_VERSION running on the
host specified by the 1st command line arg. */
clnt = clnt_create(argv[1], SIMP_PROG, SIMP_VERSION, "udp");
/* Make sure the create worked */
if (clnt == (CLIENT *) NULL) {
clnt_pcreateerror(argv[1]);
exit(1);
}
/* get the 2 numbers that should be added */
x = atoi(argv[2]);
y = atoi(argv[3]);
printf("%d + %d = %d\n",x,y, add(clnt,x,y));
printf("%d - %d = %d\n",x,y, sub(clnt,x,y));
return(0);
}
simpservice.c
/* Definition of the remote add and subtract procedure used by
simple RPC example
rpcgen will create a template for you that contains much of the code
needed in this file is you give it the "-Ss" command line arg.
*/
#include "simp.h"
/* Here is the actual remote procedure */
/* The return value of this procedure must be a pointer to int! */
/* we declare the variable result as static so we can return a
pointer to it */
int *
add_1_svc(operands *argp, struct svc_req *rqstp)
{
static int result;
printf("Got request: adding %d, %d\n", argp->x, argp->y);
result = argp->x + argp->y;
return (&result);
}
int *
sub_1_svc(operands *argp, struct svc_req *rqstp)
{
static int result;
printf("Got request: subtracting %d, %d\n", argp->x, argp->y);
result = argp->x - argp->y;
return (&result);
}
Compilation and Output
Server
vivek@ubuntu~$ rpcgen -C -a simp.x
vivek@ubuntu~$ cc -o server simpservice.c simp_svc.c simp_xdr.c
vivek@ubuntu~$ ./server
Got request: adding 4, 5
Got request: subtracting 4, 5
Client
vivek@ubuntu~$ cc -o client simpclient.c simp_clnt.c simp_xdr.c
vivek@ubuntu~$ ./client linux 4 5
4 + 5 = 9
4 - 5 = -1
Thursday, September 16, 2010
OPAC System program in Java
Develop a simple OPAC system for library using even-driven and concurrent programming paradigms of Java. Use JDBC to connect to a back-end database.
Procedure
Create a new Database file in MS ACCESS (our backend) named “books.mdb”.
Then create a table named “Library” in it.
The table Library contains the following fields and data types,
AuthorName – Text
ISBN – Text
BookName - Text
Price - Number
Publisher – Text
Enter various records as you wish.
Save the database file.
Next step is to add our “books.mdb” to the System DSN. To do that follow the procedure given below,
Go to Start-> Control Panel -> Administrative tools.
In that double click “Data Sources (ODBC)”.
ODBC Data Source Administrator dialog appears.
In that select “System DSN” tab and click the Add Button.
Select “Microsoft Access Driver(*.mdb)” and click Finish.
ODBC Microsoft Access Setup appears. In the “Data Source name” type “Library”.
Click on the “Select” button and choose your database file. Then click ok.
Now your database file gets added to the System DSN. It should look like below,
Now execute the following code “Library.java”.
import java.sql.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.table.*;
public class Library implements ActionListener
{
JRadioButton rbauthor = new JRadioButton("Search by Author name");
JRadioButton rbbook = new JRadioButton("Search by Book name");
JTextField textfld = new JTextField(30);
JLabel label = new JLabel("Enter Search Key");
JButton searchbutton = new JButton("Search");
JFrame frame = new JFrame();
JTable table;
DefaultTableModel model;
String query = "select * from Library";
public Library()
{
frame.setTitle("Online Public Access Catalog");
frame.setSize(500,600);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
JPanel p1 = new JPanel();
JPanel p2 = new JPanel();
JPanel p3 = new JPanel();
p1.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
p1.add(label);
p1.add(textfld);
ButtonGroup bg = new ButtonGroup();
bg.add(rbauthor);
bg.add(rbbook);
p2.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
p2.add(rbauthor);
p2.add(rbbook);
p2.add(searchbutton);
searchbutton.addActionListener(this);
p3.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
p3.add(p1,BorderLayout.NORTH);
p3.add(p2,BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.add(p3,BorderLayout.NORTH);
addTable(query);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
public void addTable(String s)
{
try
{
Class.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver");
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:odbc:Library","","");
Statement st = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery(s);
ResultSetMetaData md = rs.getMetaData();
int cols = md.getColumnCount();
model = new DefaultTableModel(1,cols);
table = new JTable(model);
String[] tabledata = new String[cols];
int i=0;
while(i
model.removeRow(0);
frame.remove(table);
addTable(query);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
new Library();
}
}
Screenshots of Output
(Opening Screen)
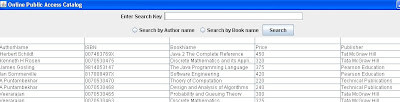
(author Search)
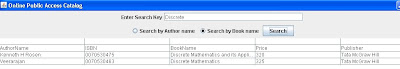
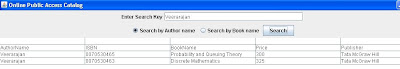 (Book Search)
(Book Search)
Download the Source Code
Library.java
Saturday, September 11, 2010
Multithreading using Pipes Program
Write a multi-threaded Java program to print all numbers below 100,000 that are
both prime and fibonacci number (some examples are 2, 3, 5, 13, etc.). Design a
thread that generates prime numbers below 100,000 and writes them into a pipe.
Design another thread that generates fibonacci numbers and writes them to another pipe. The main thread should read both the pipes to identify numbers common to both.
Program Written by Mr.G.Kumaresan sir.
Program
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Fibonacci extends Thread
{
private PipedWriter out = new PipedWriter();
public PipedWriter getPipedWriter()
{
return out;
}
public void run()
{
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
t.setName("Fibonacci");
System.out.println(t.getName() + " thread started");
int fibo1=0,fibo2=1,fibo=0;
while(true)
{
try
{
fibo = fibo1 + fibo2;
if(fibo>100000)
{
out.close();
break;
}
out.write(fibo);
sleep(1000);
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Fibonacci:"+e);
}
fibo1=fibo2;
fibo2=fibo;
}
System.out.println(t.getName() + " thread exiting");
}
}
class Prime extends Thread
{
private PipedWriter out1 = new PipedWriter();
public PipedWriter getPipedWriter()
{
return out1;
}
public void run()
{
Thread t= Thread.currentThread();
t.setName("Prime");
System.out.println(t.getName() + " thread Started...");
int prime=1;
while(true)
{
try
{
if(prime>100000)
{
out1.close();
break;
}
if(isPrime(prime))
out1.write(prime);
prime++;
sleep(0);
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(t.getName() + " thread exiting.");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
public boolean isPrime(int n)
{
int m=(int)Math.round(Math.sqrt(n));
if(n==1 || n==2)
return true;
for(int i=2;i<=m;i++)
if(n%i==0)
return false;
return true;
}
}
public class PipedIo
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
Thread t=Thread.currentThread();
t.setName("Main");
System.out.println(t.getName() + " thread Started...");
Fibonacci fibonacci = new Fibonacci();
Prime prime = new Prime();
PipedReader fpr = new PipedReader(fibonacci.getPipedWriter());
PipedReader ppr = new PipedReader(prime.getPipedWriter());
fibonacci.start();
prime.start();
int fib=fpr.read(), prm=ppr.read();
System.out.println("The numbers common to PRIME and FIBONACCI:");
while((fib!=-1) && (prm!=-1))
{
while(prm<=fib)
{
if(fib==prm)
System.out.println(prm);
prm=ppr.read();
}
fib=fpr.read();
}
System.out.println(t.getName() + " thread exiting");
}
}
Download Source Code
PipedIo.java
Tuesday, September 7, 2010
Electives for 6th Semester
of which I feel these to be better
Elective 1
We can take either CS2023(Advanced Java Programming) or IT2353(Web Technology)....Both are of use to us.
Elective 2
Ofc, Numerical Methods would be an unanimous choice....
What do you feel????? What's your choice??
Monday, September 6, 2010
Software Engineering Important Ques
Part A
1.List out the elements of Analysis Modelling. (with diagram).
2.Define Cardinality and Modality. (with diagram)
3. Compare and Contrast throw away and evolutionary prototyping.
4. Compare STD and DFD (with diagram).
5. Write the distinct steps in Requirement Engineering process.
6. Why requirement Elicitation process is difficult?
7. What are steps required to build ERD?
8. Benefits of Prototyping.
9. What is SRS, and its Characteristics.
Part B
1. Explain in detail about Requirement Engineering process.
2. Explain in detail about Data, Functional and Behavioral modelling along with diagrams.
Thursday, September 2, 2010
Anna University R 2008 November December Exam Time Table
B.E /B.Tech./B.Arch. ( V Semester ) Nov./ Dec. -2010 (R-2008)
Other Semester papers(exam Schedule) R 2008
B.E /B.Tech./B.Arch. ( IV Semester ) Nov./ Dec. -2010 (R-2008)
B.E /B.Tech./B.Arch. ( III Semester ) Nov./ Dec. -2010 (R-2008)
B.E /B.Tech./B.Arch. ( II Semester ) Nov./ Dec. -2010 (R-2008)
B.E /B.Tech./B.Arch. ( I Semester ) Nov./ Dec. -2010 (R-2008)
All the Best for your Exams....
